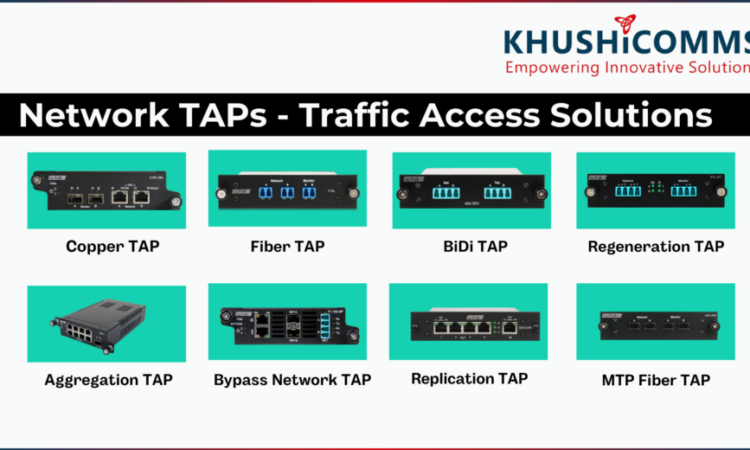
A Network TAP is a hardware device that provides a passive way to monitor network traffic without disrupting data flow. It creates an exact copy of the traffic passing through a network link, sending it to monitoring and security tools for analysis. Unlike SPAN (Switch Port Analyzer) ports, which can introduce packet loss and latency, TAPs offer 100% visibility with zero impact on network performance. https://www.khushicomms.com/category/network-taps
How Network TAPs Work
A TAP is inserted between two network devices (e.g., a switch and a router). It captures and duplicates all incoming and outgoing data, forwarding the copies to monitoring tools such as:
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)Network Performance Monitors (NPM)Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems Forensics and packet analysis tools Types of Network TAPs Different network environments require different types of TAPs. Here are the most common ones:
- Passive TAPs – Do not require power and allow uninterrupted data flow, even if the TAP fails. Ideal for fiber optic networks.
- Active TAPs – Require power and are commonly used for copper Ethernet networks. They can regenerate signals to ensure data integrity.
- Aggregation TAPs – Combine multiple network links into a single output, reducing the number of monitoring ports needed.
- Regeneration TAPs – Duplicate traffic to multiple monitoring tools, useful for large-scale analysis.
- Bypass TAPs – Help maintain network uptime by ensuring that security appliances (like firewalls) don’t become a single point of failure.
Benefits of Using Network TAPs
 Real Estate / Property
Real Estate / Property  Vehicles
Vehicles  Bikes
Bikes  Mobiles & Tablets
Mobiles & Tablets  Electronics
Electronics  Furniture & Home Decor
Furniture & Home Decor  Fashion & Beauty
Fashion & Beauty  Jobs
Jobs  Services
Services  Pets / Animals
Pets / Animals  Books, Sports & Hobbies
Books, Sports & Hobbies  Kids
Kids  Business, Industrial & Agriculture
Business, Industrial & Agriculture